Extracellular adenosine and its receptor
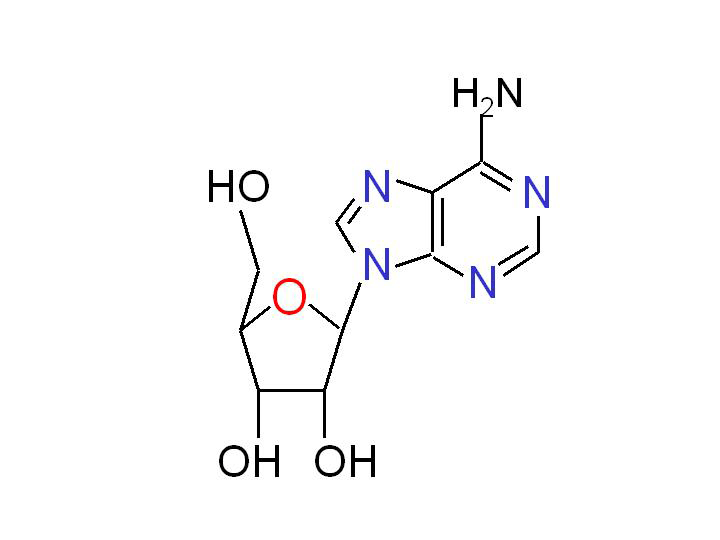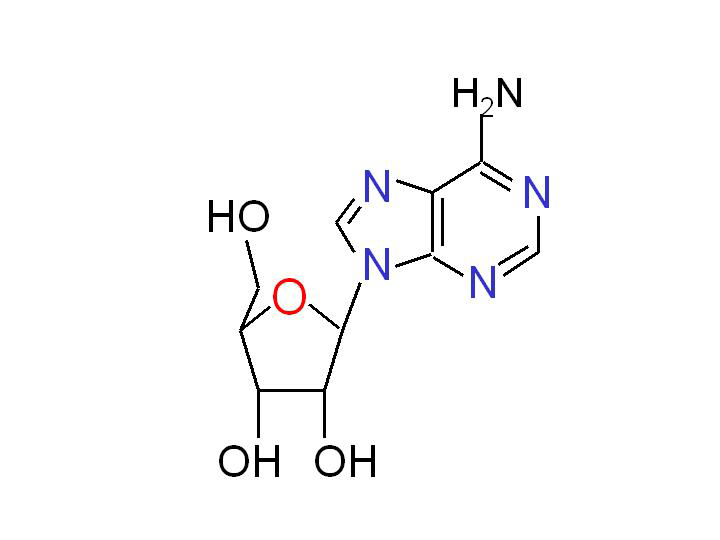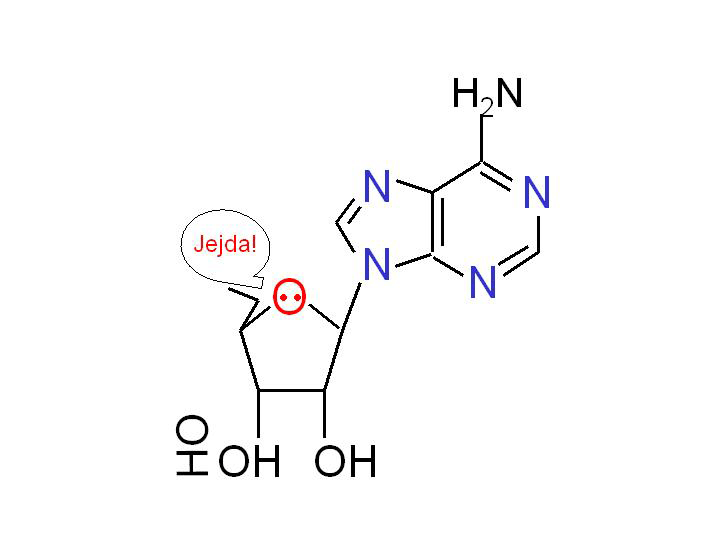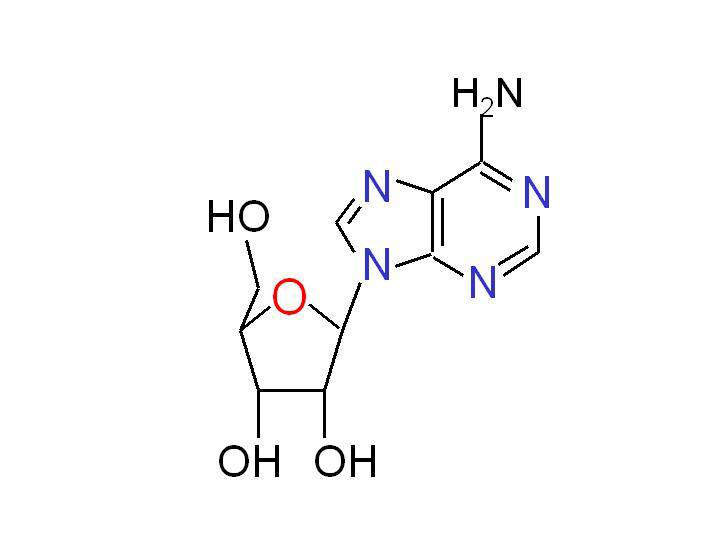 Adenosine is a multifunctional nucleoside that is most important as an intracellular precursor of nucleic acids and ATP, but it is also a key extracellular signaling molecule affecting a variety of cellular processes. The interest in adenosine as a signaling molecule goes back at least as far as 1929. It has been known since the early study of Drury and Szent-Gyorgyi that adenosine injection increased coronary blood flow, reduced heart beat rate and lowered systemic blood pressure (Drury and Szent-Gyorgyi, 1929). In later studies, the extracellular adenosine was also implicated in the regulation of immune and neural functions, as well as in the responses to stress and hypoxia.
Adenosine is a multifunctional nucleoside that is most important as an intracellular precursor of nucleic acids and ATP, but it is also a key extracellular signaling molecule affecting a variety of cellular processes. The interest in adenosine as a signaling molecule goes back at least as far as 1929. It has been known since the early study of Drury and Szent-Gyorgyi that adenosine injection increased coronary blood flow, reduced heart beat rate and lowered systemic blood pressure (Drury and Szent-Gyorgyi, 1929). In later studies, the extracellular adenosine was also implicated in the regulation of immune and neural functions, as well as in the responses to stress and hypoxia.
Four mammalian subtypes of the AdoR have been identified and their genes cloned: A1, A2A, A2B, and A3. They have been shown to modulate intracellular levels of 3', 5'-adenosine cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) in different ways: A1 and A3 inhibit adenylate cyclase, whereas A2A and A2B stimulate this enzyme (van Calker et al., 1979; Londos et al., 1980). The existence of four receptors with different functions but overlapping patterns of expression, together with the pervasiveness of adenosine- mediated physiological events, pose difficult questions in efforts to design pharmacological and biochemical interventions (Nyce, 1999).
By conducting BLAST searches of the available Drosophila protein database, we have identified CG9753 as the gene encoding the Drosophila AdoR homolog. The sequence of Drosophila AdoR is quite divergent from the mammalian AdoRs but they still share the region important for adenosine binding. Furthermore, our pharmacological experiments revealed that Drosophila AdoR functionally responds to adenosine and is able to activate at least two second messenger pathways, involving cAMP and calcium. By assaying cAMP and Ca2+ levels in CHO cells transiently transfected with Drosophila AdoR, we detected increase in both cAMP and calcium levels after adenosine treatment. In both cases, activation occurred at physiologically relevant doses, and was only present for the AdoR plasmid in sense orientation.
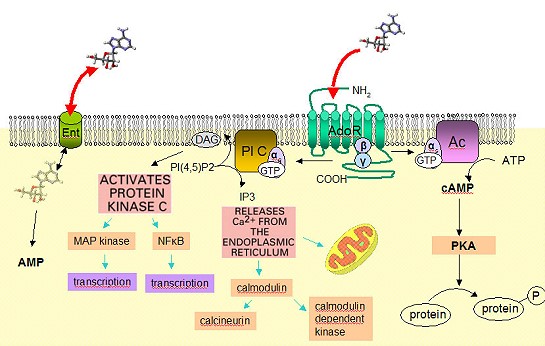

Four mammalian subtypes of the AdoR have been identified and their genes cloned: A1, A2A, A2B, and A3. They have been shown to modulate intracellular levels of 3', 5'-adenosine cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) in different ways: A1 and A3 inhibit adenylate cyclase, whereas A2A and A2B stimulate this enzyme (van Calker et al., 1979; Londos et al., 1980). The existence of four receptors with different functions but overlapping patterns of expression, together with the pervasiveness of adenosine- mediated physiological events, pose difficult questions in efforts to design pharmacological and biochemical interventions (Nyce, 1999).
By conducting BLAST searches of the available Drosophila protein database, we have identified CG9753 as the gene encoding the Drosophila AdoR homolog. The sequence of Drosophila AdoR is quite divergent from the mammalian AdoRs but they still share the region important for adenosine binding. Furthermore, our pharmacological experiments revealed that Drosophila AdoR functionally responds to adenosine and is able to activate at least two second messenger pathways, involving cAMP and calcium. By assaying cAMP and Ca2+ levels in CHO cells transiently transfected with Drosophila AdoR, we detected increase in both cAMP and calcium levels after adenosine treatment. In both cases, activation occurred at physiologically relevant doses, and was only present for the AdoR plasmid in sense orientation.